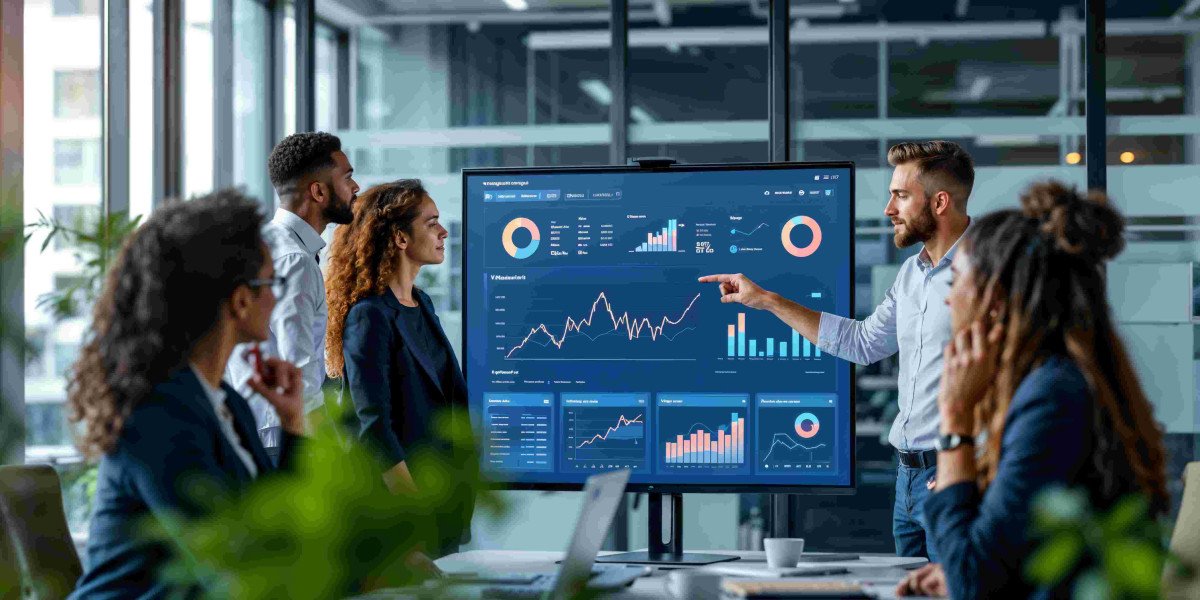
The complexity of modern business operations demands integrated technology platforms that unify disparate processes, eliminate information silos, and provide comprehensive visibility across organizational functions. ERP and CRM software solutions serve as the central nervous system of contemporary enterprises, coordinating activities, facilitating communication, and enabling data-driven decision-making that drives competitive performance. Organizations implementing centralized business management platforms position themselves to operate with greater agility, efficiency, and strategic clarity than competitors relying on fragmented legacy systems.
The Evolution Toward Centralized Business Management
Historical business software landscapes consisted of disconnected point solutions addressing specific functional needs—separate systems for accounting, inventory, sales, customer service, and human resources. While each system excelled within its domain, the lack of integration created numerous challenges: data inconsistencies across systems, manual data re-entry consuming valuable time, delayed access to critical information, and incomplete visibility into business performance.
ERP and CRM software integration addresses these challenges by creating unified platforms where information flows seamlessly across functional boundaries. When sales representatives close deals, the information immediately becomes available to finance for invoicing, operations for fulfillment, and service teams for onboarding support. This real-time information flow eliminates delays, reduces errors, and enables coordinated execution that enhances customer experiences and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Customer Relationship Management
Centralized CRM functionality provides complete visibility into every customer interaction, from initial marketing touchpoints through sales conversations, service requests, and ongoing relationship management. Marketing teams track campaign performance, lead generation effectiveness, and content engagement, passing qualified leads to sales with comprehensive context about interests, behaviors, and preferences that inform effective sales approaches.
Sales teams benefit from ERP and CRM software integration that provides instant access to product availability, pricing information, customer order history, and payment terms without switching between systems or contacting other departments. This immediate access accelerates sales cycles, improves quote accuracy, and enables sales representatives to focus on relationship building rather than administrative coordination.
Customer service excellence depends on comprehensive information access, and centralized platforms provide support teams with complete customer histories including purchases, previous service interactions, outstanding issues, and account status. This comprehensive context enables personalized service that resolves issues efficiently while identifying opportunities for proactive outreach that prevents problems and strengthens relationships.
Enterprise Resource Planning for Operational Control
Financial management within centralized ERP and CRM software platforms provides real-time visibility into organizational financial health, automating transaction processing, reconciliation, and reporting while maintaining compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. Integration across operational systems ensures financial records accurately reflect business activities without manual reconciliation processes that introduce delays and potential errors.
Supply chain management functionality optimizes inventory investment while ensuring product availability meets customer demands and production requirements. Centralized systems provide visibility into inventory levels across multiple locations, track materials in transit, coordinate replenishment activities, and enable transfer between locations to optimize overall inventory position while minimizing stockouts and excess inventory carrying costs.
Manufacturing operations benefit from ERP and CRM software that coordinates production scheduling, materials management, capacity planning, and quality control within unified platforms. Production schedules reflect actual customer orders and inventory positions, material requirements planning ensures component availability, and quality metrics flow directly into continuous improvement initiatives without requiring separate data collection and analysis processes.
Project Management and Resource Allocation
Project-based organizations require sophisticated resource allocation, time tracking, and project accounting capabilities that centralized platforms provide. Project managers gain visibility into resource availability, skill sets, and current commitments, enabling informed assignment decisions that balance workload distribution with project requirements and delivery timelines.
Time and expense tracking integrated with project management and financial systems ensures accurate project costing, enables profitability analysis, and supports client billing processes. When employees record time against projects within centralized ERP and CRM software, that information automatically flows into payroll processing, project accounting, client invoicing, and resource utilization reporting without manual data transfer or reconciliation.
Business Intelligence and Reporting
Centralized platforms transform operational data into strategic insights through comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities. Customizable dashboards provide role-specific views of key performance indicators, enabling stakeholders at all organizational levels to monitor metrics relevant to their responsibilities and make informed decisions based on current, accurate information.
Cross-functional reporting leverages the integration inherent in ERP and CRM software platforms to analyze business performance across traditional departmental boundaries. Organizations can examine profitability by customer, product, region, or sales representative; analyze customer lifetime value considering all interactions and transactions; and identify trends that span multiple business functions, revealing opportunities and risks that isolated systems would obscure.
Workflow Automation and Process Optimization
Centralized platforms enable sophisticated workflow automation that streamlines routine processes, enforces business rules, and ensures consistent execution across the organization. Approval workflows route purchase requisitions, expense reports, and other requests to appropriate authorities based on business rules, maintaining appropriate controls while minimizing delays and administrative overhead.
Automated notifications keep stakeholders informed about events requiring attention, such as low inventory levels, customer service issues exceeding resolution targets, or sales opportunities requiring follow-up. By proactively alerting relevant personnel, ERP and CRM software systems prevent issues from escalating while enabling timely responses that maintain customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Scalability and Growth Support
Organizations implementing centralized business management platforms invest in infrastructure that supports growth without requiring disruptive system replacements as business expands. Cloud-based ERP and CRM software solutions scale seamlessly to accommodate increasing transaction volumes, additional users, new business locations, and expanded product lines without the capacity constraints that plague on-premises legacy systems.
Multi-entity and multi-currency capabilities enable organizations to expand internationally while maintaining centralized visibility and control. Subsidiary financial results consolidate automatically for corporate reporting, while local operations maintain autonomy to operate according to regional requirements and regulations. This balance of central control and local flexibility enables effective global operations within unified technology platforms.
Collaboration and Communication Enhancement
Modern ERP and CRM software platforms incorporate collaboration features that facilitate communication and coordination across teams, departments, and geographic locations. Document sharing, discussion threads, and activity feeds keep project teams aligned, while notification systems ensure stakeholders remain informed about relevant developments without overwhelming them with irrelevant information.
Customer-facing portals extend platform capabilities to customers and partners, enabling self-service access to order status, invoices, support resources, and account information. By providing convenient access to information customers need, organizations reduce support costs while improving customer satisfaction through immediate access to accurate information.
Mobile Access and Remote Productivity
The distributed nature of modern workforces necessitates mobile access to business systems, enabling productivity from any location. Sales representatives update opportunities immediately following customer meetings, field service technicians access work orders and update job status from customer sites, and executives monitor business performance while traveling, all through mobile-optimized interfaces within centralized ERP and CRM software platforms.
Offline capabilities ensure productivity continues even when internet connectivity becomes unavailable, with automatic synchronization when connections restore. This reliability proves essential for organizations with remote workers, field operations, or international teams operating across regions with varying infrastructure quality.
Security, Privacy, and Compliance
Centralized platforms simplify security management by consolidating access controls, authentication, and authorization within unified systems rather than managing separate security policies across multiple applications. Role-based permissions ensure users access only information necessary for their responsibilities, while comprehensive audit trails maintain records of system access and data modifications for compliance and security monitoring.
Data privacy regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific requirements demand careful attention to how customer and employee information is collected, stored, processed, and shared. ERP and CRM software platforms built with privacy considerations enable organizations to meet regulatory obligations through features such as data encryption, consent management, data retention policies, and subject access request fulfillment.
Implementation Success Factors
Successful centralized platform implementation requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and change management that prepares organizations for new processes and ways of working. Organizations should begin with clear objectives, documented requirements, and realistic timelines that account for data migration, system configuration, integration development, testing, and user training.
Executive sponsorship proves critical for implementation success, providing authority to make difficult decisions, allocate necessary resources, and drive adoption across organizational resistance. Change management activities that communicate benefits, address concerns, and provide comprehensive training ensure users understand new capabilities and adopt workflows that realize intended benefits.
Conclusion
ERP and CRM solutions that centralize business management represent transformative investments enabling organizations to operate with unprecedented coordination, visibility, and efficiency. By unifying customer relationships, financial management, operations, and human capital within integrated platforms, businesses eliminate information silos, streamline processes, and position themselves for sustainable competitive advantage in dynamic markets demanding operational excellence and customer-centric execution.